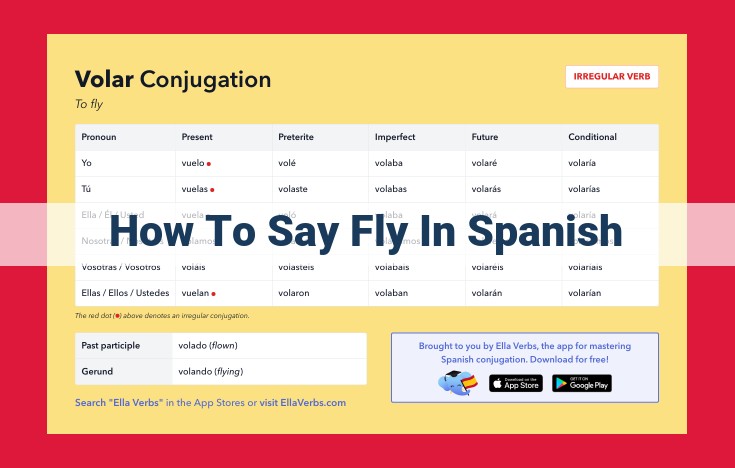
To say “fly” in Spanish, use the verb “volar,” pronounced “boh-lar.” It can be conjugated depending on the subject: “yo vuelo” (I fly), “tú vuelas” (you fly), “él/ella/usted vuela” (he/she/you formal fly), “nosotros volamos” (we fly), “vosotros voláis” (you plural informal fly), and “ellos/ellas/ustedes vuelan” (they/you plural formal fly).
Aviation: Soaring the Skies
A Tale of Human Ingenuity
From the earliest dreams of flight to modern marvels, aviation has captivated the human imagination. The Wright brothers’ daring first flight in 1903 was not merely a milestone in aviation, but a testament to humanity’s indomitable spirit. Over the past century, aviation has evolved from a daring adventure to an integral part of our global transportation system.
The pioneers of aviation faced immense challenges: flimsy aircraft, unreliable engines, and unpredictable weather. Yet, their determination and unwavering belief in the power of flight pushed the boundaries of human knowledge and technology. Today, we marvel at the sleek jets that traverse the skies, connecting continents in mere hours.
Beyond Transportation: The Significance of Aviation
Aviation plays a pivotal role in facilitating global trade, tourism, and cultural exchange. Airports serve as gateways to cities and nations, fostering connections and stimulating economic growth. Moreover, aviation enables humanitarian aid to reach remote regions, provides medical evacuations, and facilitates disaster relief efforts.
The military also relies heavily on aviation for reconnaissance, surveillance, and transportation. During wartime, aircraft have proven invaluable in protecting national interests and delivering decisive blows. In short, aviation has become an indispensable tool for human progress and well-being.
Types of Aircraft: Discuss the diverse categories of aircraft, including fixed-wing planes, helicopters, and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs).
Types of Aircraft: Conquering the Skies
Aviation has soared to new heights with an array of aircraft that dominate the skies. From fixed-wing planes soaring through the air with unwavering grace to the versatility of helicopters, these machines have transformed our ability to travel and explore.
Fixed-Wing Planes: Masters of Aerodynamics
Fixed-wing planes harness the principles of aerodynamics to conquer the heavens. Their streamlined bodies and swept-back wings reduce drag, allowing them to glide effortlessly through the air. From commercial airliners transporting millions of passengers to military jets breaking the sound barrier, fixed-wing planes are the backbone of global aviation.
Helicopters: Unbound by Runways
Unlike fixed-wing planes, helicopters defy the need for runways. Their rotating blades provide lift and maneuverability, making them indispensable for search and rescue operations, law enforcement, and military missions. Their vertical takeoff and landing capabilities allow them to access remote areas and confined spaces.
Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs): Eyes in the Sky
Unmanned Aerial Vehicles, commonly known as drones, have revolutionized aerial surveillance and data collection. These autonomous aircraft operate without a human pilot, relying on advanced sensors and GPS to navigate and perform tasks. UAVs have become essential tools for military reconnaissance, disaster response, and commercial applications such as aerial photography and mapping.
Aviation Infrastructure: The Backbone of Soaring Skies
The world of aviation unfolds its wings upon a tapestry of critical infrastructure, without which the graceful dance of aircraft would become a mere dream. At the heart of this intricate ecosystem lies the airport, a bustling hub where dreams of flight take off and land. Modern airports, like intricate masterpieces of engineering, orchestrate the seamless flow of passengers, aircraft, and cargo.
Towering above the airport’s landscape, the air traffic control system stands as the watchful sentinel, guiding aircraft through the intricate dance of the heavens. With precision and unwavering diligence, air traffic controllers monitor the aerial ballet, ensuring the safety and efficiency of every flight. Their voices, a reassuring beacon in the sky, coordinate the paths of aircraft, like celestial navigators charting the course of airborne journeys.
Completing the trinity of essential aviation infrastructure components are the airlines. These aerial pioneers connect distant lands and forge bonds between cultures. From sleek commercial jets to chartered aircraft, airlines play a pivotal role in shaping the tapestry of global travel. Their fleets crisscross the globe, carrying dreams, aspirations, and countless stories within their wings.
These three pillars of aviation infrastructure, intertwined like threads in an aeronautical tapestry, provide the foundation upon which the wings of progress soar. Airports, air traffic control, and airlines form the backbone of this soaring symphony, enabling us to embrace the boundless realm of aviation.
Aviation Careers: The Sky’s the Limit for Aspiring Aviators
Soaring the Skies with Purpose and Passion
Aviation isn’t merely about navigating the vast expanse above; it’s a field teeming with diverse and fulfilling careers that offer a unique blend of skill, adventure, and impact. From the captains who command the heavens to the unsung heroes who keep the skies safe and efficient, aviation careers are a testament to human ingenuity and the pursuit of flight.
Take the Controls: The Role of Pilots
At the helm of every aircraft lies the pilot, the orchestrator of every aerial symphony. With an unwavering focus and steady hand, they navigate the skies, ensuring the safety and comfort of passengers or executing precise maneuvers for specialized missions. As a pilot, you’ll master the art of flight, making split-second decisions, and managing complex systems while enjoying unparalleled views from your cockpit window.
Ensuring a Smooth Journey: Flight Attendants
In the heart of every aircraft, flight attendants are the embodiment of hospitality and safety. With grace and warmth, they assist passengers, providing comfort, reassurance, and essential instructions during flights. As a flight attendant, you’ll be the face of the airline, creating a welcoming and memorable experience for those sharing your airborne journey.
Engineers: The Unsung Heroes of Aviation
Behind the scenes of every successful flight lie the tireless efforts of engineers. They design, maintain, and troubleshoot aircraft, ensuring their airworthiness and smooth operation. From sleek aerodynamics to intricate electrical systems, engineers play a critical role in keeping the skies safe and reliable.
Guiding the Skies: Air Traffic Controllers
High above the ground, orchestrating the flow of aircraft, are air traffic controllers. With precision and focus, they monitor and guide pilots, ensuring safe and efficient navigation. As an air traffic controller, you’ll possess a keen eye for detail, a quick mind, and an unwavering commitment to safety, safeguarding the skies for millions of air travelers.
Embark on Your Aviation Career Adventure
Whether you aspire to soar as a pilot, provide exceptional service as a flight attendant, innovate as an engineer, or guide the skies as an air traffic controller, aviation offers a myriad of rewarding career paths. Join the ranks of dedicated aviation professionals who share a passion for flight and a commitment to excellence. Explore the skies and pursue your dreams in an industry that continues to inspire and amaze.
Commercial and Private Aviation: Contrasting Worlds of Flight
In the vast expanse of the skies, two distinct realms of aviation intertwine: commercial and private. Each serves a unique purpose and operates under different regulations, shaping the very fabric of air travel.
Commercial Aviation: Wings of Commerce and Connectivity
- Purpose: Transporting passengers and cargo on scheduled services connecting cities and nations, facilitating global trade and tourism.
- Regulation: Rigorously regulated by government agencies to ensure safety, security, and adherence to international standards.
- Infrastructure: Relies on sprawling airport hubs, advanced air traffic control systems, and extensive maintenance facilities.
- Careers: Offers a wide range of professional opportunities, from pilots and flight attendants to ground staff and management personnel.
In commercial aviation, the emphasis lies on reliability, efficiency, and affordability. Airlines meticulously plan flight schedules, optimize routes, and constantly innovate to enhance passenger experience and minimize costs. They operate a diverse fleet of aircraft, from narrow-body regional jets to wide-body airliners that traverse continents.
Private Aviation: Freedom and Flexibility in the Air
- Purpose: Provides tailored air transport services for individuals, corporations, and niche markets.
- Regulation: Less stringent regulations compared to commercial aviation, allowing for greater flexibility and customization.
- Infrastructure: Utilizes smaller airports, private airstrips, and specialized maintenance providers.
- Careers: Focuses on specialized roles such as personal pilots, aircraft management, and charter brokerage.
Private aviation offers discerning travelers the ultimate in convenience, privacy, and personalized service. They can charter aircraft on demand, select specific departure and arrival times, and enjoy the comfort of private airport lounges. It enables businesses to conduct meetings in flight, access remote locations, and optimize executive travel.
Contrasting Regulations
The regulations governing commercial and private aviation serve to ensure safety, fair competition, and environmental protection. While both must adhere to fundamental flight safety standards, private aviation enjoys some flexibility in terms of maintenance schedules, crew training requirements, and operational restrictions.
For commercial airlines, the emphasis is on stringent compliance with rigorous safety and security protocols. They undergo regular inspections, audits, and training programs to maintain the highest levels of airworthiness.
In contrast, private aircraft owners may have more autonomy in scheduling maintenance and training. However, they must still adhere to minimum safety standards set by aviation authorities. This regulatory balance allows private aviation to offer greater flexibility while maintaining a strong commitment to safety.
Non-Powered Flight: Gliding Through the Skies Without Engines
Embark on an exhilarating journey into the realm of non-powered flight, where humans and nature intertwine to conquer the skies. In this domain, the absence of engines gives way to a profound connection between aviators and the elements.
Soaring beckons brave pilots to harness the wind’s invisible currents, gliding effortlessly through the heavens. Like eagles soaring on high, they ride the updrafts, gaining altitude with each graceful ascent.
Paragliding invites thrill-seekers to take to the skies with only a canopy and their own daring. Guided by the wind’s whims, they soar over landscapes, experiencing the freedom of flight in its purest form.
Whether it’s the silent majesty of soaring or the adrenaline-pumping rush of paragliding, non-powered flight offers a unique perspective on the world. It’s a testament to human ingenuity and the enduring allure of the skies.
Evolution and Adaptation: Discuss the remarkable adaptations of birds for flight, including specialized wings, feathers, and flight muscles.
Evolution and Adaptation: Birds’ Marvelous Flight Mechanisms
Beneath the azure expanse, birds soar effortlessly, captivating our imaginations with their aerial prowess. Their ability to navigate the skies is a testament to millions of years of evolution and remarkable adaptations.
Specialized Wings:
At the heart of birds’ flight is their streamlined wings. These structures are composed of lightweight bones and feathers, arranged to create an airfoil shape. As birds flap their wings, the curved upper surface generates lift, propelling them through the air.
Feathers:
Feathers, a unique characteristic of birds, play a crucial role in flight. Their lightweight, yet strong shafts provide support and flexibility. The intricate arrangement of vanes creates a smooth surface, reducing drag and allowing for efficient movement through the air.
Flight Muscles:
Powerful flight muscles, present in birds’ chests, provide the force required for flapping. These muscles are specialized for rapid contractions, enabling birds to generate the necessary thrust for takeoff, flight, and landing.
Bird Physiology: The Wonders of Avian Flight
Like remarkable aerial acrobats, birds soar through the skies, their _flight_a testament to the extraordinary adaptations that nature has bestowed upon them. To fully appreciate the mechanics of avian flight, let’s delve into the unique physiological systems that empower these feathered marvels.
Respiratory System: A Symphony of Oxygen Exchange
Birds’ respiratory system is tailored to support their energetic flight. Air sacs, located throughout their body, act as billowing reservoirs, collecting and storing oxygen. With each inhalation, fresh air flows directly into these sacs, while exhaled air is efficiently expelled through a complex network of one-way airways. This remarkable system ensures a continuous supply of oxygen even during demanding aerial maneuvers.
Circulatory System: A Pumping Powerhouse
The avian circulatory system is a masterpiece of efficiency, ensuring a steady supply of oxygen and nutrients to every part of their bodies. Their hearts, relatively larger than mammalian hearts in proportion to body size, pump oxygenated blood through a robust network of blood vessels. Capillaries, the tiniest of these vessels, extend deep into the flight muscles, providing the fuel necessary for sustained flight.
Skeletal System: Lightweight and Strong
The skeletal system of birds is both lightweight and remarkably strong. Their bones, hollow and reinforced with struts, provide rigidity and support without adding unnecessary weight. This combination of strength and lightness is essential for efficient and agile flight. The unique arrangement of their_ muscles_ allows birds to generate the powerful force needed for takeoff, flapping, and maneuvering.
Through these remarkable physiological adaptations, birds have mastered the art of flight. Their respiratory, circulatory, and skeletal systems work in perfect harmony, enabling them to soar through the skies with grace and agility. These intricate adaptations are a testament to the wonders of nature’s design and the boundless possibilities of life in the avian realm.
Flight Techniques: Mastering the Skies
In the avian kingdom, flight is an art form that defies gravity. Birds possess an array of specialized flight techniques that enable them to conquer the skies with grace and precision.
Soaring: The Silent Gliders
Soaring birds, like eagles and vultures, have long, slender wings that maximize lift. They use updrafts and thermal currents to soar effortlessly for hours on end, covering vast distances without flapping a wing.
Flapping: The Power of Propulsion
Flapping birds, including sparrows, robins, and hawks, generate lift and thrust by rapidly beating their wings. The shape and frequency of their wing beats vary depending on their speed, altitude, and maneuverability needs.
Gliding: A Gravitational Dance
Gliding birds, such as albatrosses and pelicans, take advantage of their streamlined bodies and feather design to maintain flight. They spread their wings and glide with minimal effort, often traveling long distances over open water.
Specialized Flight Adaptations
Each flight technique is tailored to the specific needs and habitats of different bird species. Soaring birds have evolved lightweight bones and powerful muscles for extended flight. Flapping birds boast strong wing muscles and flexible joints for agility and quick maneuvering. Gliding birds possess large, wingspan that act as efficient sails.
By mastering these diverse flight techniques, birds have carved a niche for themselves as the aerial rulers of our planet. From soaring eagles to gliding albatrosses, their ability to navigate the skies is a testament to nature’s boundless ingenuity.
Bird Migration: Navigating the Skies
The Avian Odyssey
In the realm of nature’s wonders, bird migration stands as an extraordinary spectacle, a testament to the incredible adaptability and navigational abilities of our feathered friends. These seasonal journeys, undertaken by countless bird species across vast distances, are a mesmerizing display of instinct and biological precision.
Navigating the Unknown
How do these avian travelers possess the remarkable ability to navigate their intricate routes with such accuracy? Their navigational prowess is a complex interplay of innate instincts, sensory cues, and cognitive maps. Birds possess an internal compass that helps them align with Earth’s magnetic field, guiding them along their predetermined paths. Additionally, they use celestial cues, such as the position of the sun and stars, to determine their direction.
Incredible Distances and Epic Journeys
The distances traveled by migratory birds are staggering. The Arctic Tern, for instance, embarks on the longest migration of any bird, completing an annual journey of over 49,000 miles between its breeding grounds in the Arctic and its wintering grounds in Antarctica. Other notable migrants include the Bar-headed Goose, which flies over the towering heights of the Himalayas, and the Sooty Shearwater, which covers immense distances over the open ocean.
Navigational Challenges
Despite their remarkable navigational abilities, bird migration is not without its challenges. Environmental factors, such as strong winds and storms, can disrupt their flight paths, forcing them to adapt and find alternative routes. Birds also face threats from habitat loss, hunting, and climate change, which can impact their migration patterns and survival.
Ecological Importance
Bird migration plays a crucial role in maintaining ecological balance. Migratory birds transport nutrients and pollinate plants, contributing to the health of ecosystems worldwide. They also serve as predators, helping to regulate insect populations and maintain biodiversity.
Bird migration is a testament to the extraordinary resilience and adaptability of the natural world. These avian navigators, guided by their innate instincts and remarkable sensory cues, undertake epic journeys that connect continents and inspire wonder in all who witness it. Their journeys remind us of the interconnectedness of our planet and the importance of protecting these magnificent creatures for generations to come.
Birds of Prey: Nature’s Winged Predators
In the realm of aviation, we delve into the world of raptors, the fierce and majestic birds of prey. These avian predators possess an arsenal of adaptations that have honed their hunting skills for millennia.
Their keen eyesight allows them to spot prey from great distances, while their hooked beaks and powerful claws enable them to capture and subdue their victims with deadly precision.
The flight techniques employed by birds of prey are equally impressive. Some, like eagles, soar effortlessly on thermals, scanning the landscape below for unsuspecting prey. Others, such as hawks, engage in swift aerial maneuvers, swooping down on their quarry with incredible speed.
From the peregrine falcon, renowned for its record-breaking dive speeds, to the great horned owl, a master of nocturnal hunting, each raptor has evolved specific traits that optimize their predatory abilities.
Their ecological roles are as crucial as they are fascinating. Birds of prey regulate populations of smaller animals, keeping ecosystems in balance. By controlling rodent and insect numbers, they protect crops and vegetation. Moreover, their presence serves as an indicator of environmental health.
As we witness the aerial acrobatics of these avian predators, we marvel at the natural wonders that continue to inspire our understanding of flight and the delicate balance of our planet.
Songbirds: Melodious Masters of the Skies
Within the avian kingdom, the melodious voices of songbirds reverberate through the air, creating a symphony that enchants both nature enthusiasts and budding ornithologists alike. These feathered prodigies captivate with their remarkable diversity, intricate communication abilities, and profound cultural significance.
Diversity of Songbirds
The realm of songbirds is vast and varied, with over 4,000 species adorning the world’s ecosystems. From the tiny hummingbird, flitting with ethereal grace, to the majestic nightingale, whose nocturnal serenades inspire awe, the diversity of songbirds is a testament to the boundless creativity of nature.
Communication through Song
Song is the primary mode of communication among songbirds. Each species possesses a unique repertoire of melodies and calls, allowing individuals to identify mates, defend territories, and convey various emotional states. Through their intricate vocalizations, songbirds establish a complex language that fosters social cohesion and survival.
Cultural Significance
Since ancient times, songbirds have played a pivotal role in human cultures. In folklore and mythology, they often symbolize messengers or bringers of good luck. Their melodious songs have inspired countless works of art, literature, and music, becoming an integral part of human artistic expression.
Songbirds, with their enchanting voices, extraordinary diversity, and rich cultural significance, are a testament to the wonders of the natural world. Their presence enriches our environment, providing a chorus of melodies that uplift our spirits and remind us of the beauty that surrounds us. As we continue to explore and appreciate these avian maestros, may we always cherish the harmonious symphony they bring to our world.