Blog Post Outline
1. Primary Factors Influencing Emotional Experience
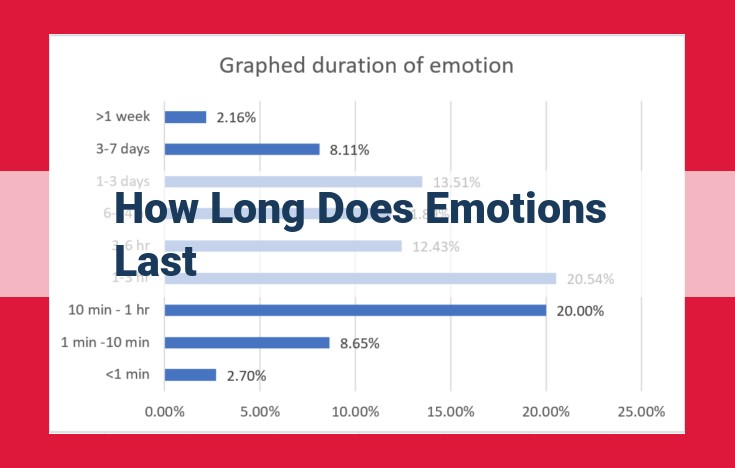
- Discuss the different types of emotions based on their duration: transient, short-lived, extended, and chronic.
2. Secondary Factors Influencing Emotional Experience
- Describe the intensity of emotions and how it can affect their impact.
3. Additional Factors
- Analyze the role of cognitive appraisal in shaping our emotional responses.
Decoding the Spectrum of Emotions: Navigating Transient, Short-Lived, Extended, and Chronic Experiences
Emotions are vibrant threads woven into the tapestry of human experience, painting our lives with a kaleidoscope of feelings. From fleeting joy to enduring sadness, they sculpt our thoughts, shape our actions, and define who we are. Understanding the different types of emotions based on their duration is essential for navigating the ebb and flow of our emotional landscape.
Transient Emotions: Fleeting Moments of Delight and Dismay
Transient emotions, like lightning flashes in the twilight, illuminate our consciousness for mere instants. Joy, anger, and surprise belong to this ephemeral realm, their presence as brief as the flicker of a candle flame. These fleeting sensations color our lives with moments of intense delight or momentary distress, before fading into the shadows.
Short-Lived Emotions: A Symphony of Joy and Sorrow
Short-lived emotions, more enduring than their transient counterparts, linger for minutes or hours, painting our day with vibrant hues of joy, sadness, or anxiety. Like a gentle breeze rustling through leaves, they create a subtle soundtrack to our lives. These emotions often stem from specific events or interactions, and their intensity usually diminishes as time goes by.
Extended Emotions: Prolonged Experiences of Joy or Distress
Extended emotions, like slow-moving rivers, flow steadily for days or even weeks. Contentment, grief, and loneliness are examples of these enduring states, their presence casting a persistent shadow or illuminating our lives with a warm glow. Unlike their short-lived counterparts, extended emotions require more conscious effort to regulate, as they become deeply entwined with our thoughts and experiences.
Chronic Emotions: The Weight of Enduring Distress
Chronic emotions, like relentless storms that never seem to abate, cast a heavy burden upon our hearts and minds. Depression, anxiety, and chronic stress belong to this oppressive category, their relentless presence overshadowing our lives for months or even years. These emotions can drain our energy, impair our functioning, and make it difficult to find joy or meaning in life.
Emotional Regulation: The Key to Managing Our Emotional Rollercoaster
Have you ever felt like the emotional tides were dragging you under? Emotional experiences can be a powerful force, shaping our thoughts, behaviors, and overall well-being. Understanding the concept of emotional regulation and its role in managing these experiences is crucial for navigating the complexities of our emotional landscape.
What is Emotional Regulation?
Emotional regulation is the ability to manage our emotions effectively. It involves recognizing and accepting our emotions, understanding their triggers, and developing strategies to respond to them in healthy ways. Emotional regulation is like a thermostat for our emotions, helping us maintain a comfortable emotional temperature amidst the ups and downs of life.
Why Emotional Regulation Matters
Emotional regulation plays a pivotal role in our mental well-being and overall functioning. It allows us to:
- Cope with stress and adversity: Regulating our emotions during challenging times helps us stay focused, make sound decisions, and protect our mental health.
- Build healthy relationships: Emotional regulation fosters empathy, compassion, and the ability to communicate our feelings respectfully.
- Enhance productivity: Managing our emotions effectively improves concentration, motivation, and performance at work or school.
- Promote physical health: Research suggests that emotional regulation can regulate stress responses, which can lower the risk of stress-related illnesses.
Developing Emotional Regulation Skills
Developing emotional regulation skills is an ongoing journey that requires practice and self-awareness. Here are a few strategies to get started:
- Identify your triggers: Recognize the situations or thoughts that tend to provoke strong emotions.
- Challenge negative thoughts: Question and reframe distorted thoughts that fuel unhelpful emotions.
- Practice mindfulness: Pay attention to your emotions without judgment, allowing them to flow through you without overwhelming you.
- Engage in relaxation techniques: Deep breathing, meditation, or yoga can help calm the nervous system and promote emotional balance.
- Seek support when needed: Don’t hesitate to reach out to a trusted friend, family member, or therapist if you’re struggling to regulate your emotions.
Remember, developing emotional regulation skills takes time and effort, but its benefits are immeasurable. By taking ownership of our emotional experiences, we empower ourselves to navigate life’s challenges with resilience, clarity, and renewed well-being.
The Intensity of Emotions: A Profound Influence
Emotions are not merely labels we attach to subjective experiences; they are powerful forces that shape our thoughts, behaviors, and overall well-being. Intensity is an inherent quality of emotions that can profoundly impact their impact on our lives.
Imagine standing on the edge of a vast ocean. The gentle lapping of small waves against the shore might evoke a sense of calm and serenity. However, as the waves grow in size and intensity, so too does our emotional response. The thunderous roar of crashing waves can instill a sense of awe, excitement, or even fear.
Similarly, in the realm of our emotions, intensity acts as an amplifier. Mild emotions, like contentment or amusement, may barely ripple the surface of our consciousness. Intense emotions, on the other hand, such as grief, joy, or anger, can overwhelm us, consuming our thoughts and actions.
Intense emotions can have a transformative effect on our lives. Powerful emotions of gratitude or compassion can inspire acts of kindness and generosity. Overwhelming emotions of grief or trauma can lead to profound personal growth or, if left unchecked, can cripple our well-being.
Understanding the relationship between intensity and emotional impact is crucial for our emotional health. By learning to regulate the intensity of our emotions, we can harness their power for personal growth and fulfillment while mitigating their potential for harm.
Emotional Intelligence: The Key to Understanding and Managing Our Emotions
In the tapestry of human experience, emotions play a vibrant and multifaceted role. They color our perceptions, drive our behaviors, and shape our relationships. While certain factors influence our emotional landscape, one skill stands out as pivotal in navigating the complexities of our emotions: emotional intelligence.
Emotional intelligence is a vital ability that allows us to recognize, understand, and manage our own emotions, as well as those of others. It’s not merely about feeling emotions; it’s about being conscious of them, interpreting them accurately, and responding in a constructive manner.
Possessing a high degree of emotional intelligence empowers us to identify and label our feelings, acknowledge their intensity, and discern the underlying causes. This self-awareness enables us to regulate our emotions, preventing them from overwhelming us and clouding our judgment.
Moreover, emotional intelligence fosters empathy, enabling us to perceive and understand the emotions of those around us. This intuitive ability allows us to build stronger relationships, communicate effectively, and create a more harmonious social environment.
By cultivating emotional intelligence, we gain the power to harness our emotions for personal growth and well-being. We can channel our positive emotions to inspire and motivate ourselves and others, while managing negative emotions in a healthy and constructive manner.
Emotional intelligence is not merely a gift; it is a skill that can be developed and strengthened through practice. By engaging in activities that enhance self-awareness, such as mindfulness, journaling, and seeking feedback from trusted individuals, we can cultivate this essential ability and reap its transformative benefits.
Emotional Exhaustion: A Hidden Peril for Your Mental Well-being
Emotions are an intrinsic part of the human experience, shaping our thoughts, actions, and interactions. While emotions can enrich our lives, they can also take a toll on our mental well-being if not adequately managed.
One insidious threat to our mental health is emotional exhaustion, a chronic state where we feel depleted, drained, and unable to cope with even minor emotional challenges. Emotional exhaustion often stems from prolonged exposure to stressful situations or the accumulation of unchecked emotions.
The consequences of emotional exhaustion can be far-reaching and debilitating. It can manifest as a sense of emptiness, a lack of motivation, and an inability to concentrate. As emotional exhaustion worsens, it can lead to burnout, depression, and even physical ailments.
The impact of emotional exhaustion on mental well-being is undeniable. It impairs our ability to think clearly, make decisions, and maintain healthy relationships. It can also lead to withdrawal from social activities and a sense of isolation.
Recognizing the signs of emotional exhaustion is crucial for preventing its harmful effects. Common symptoms include persistent fatigue, irritability, difficulty sleeping, and a diminished sense of pleasure. If you find yourself experiencing these symptoms, it’s essential to take steps to address them before they escalate.
Managing emotional exhaustion involves both preventative and interventional measures. Prioritizing self-care, setting boundaries, and practicing mindfulness can help prevent its onset. Additionally, seeking professional help from a therapist or counselor can provide support and guidance in developing effective coping mechanisms.
Remember, emotional exhaustion is not a sign of weakness but rather a consequence of prolonged emotional strain. By understanding its causes and consequences, we can take proactive steps to protect our mental well-being and maintain a healthy emotional balance.
The Role of Cognitive Appraisal in Shaping Our Emotional Responses
Emotions are not merely fleeting experiences; they are intricately interwoven with our thoughts and perceptions. The process of cognitive appraisal plays a pivotal role in shaping the intensity and nature of our emotional responses.
Imagine yourself stranded on a deserted island. The initial shock and fear you experience stem from your appraisal of the situation as threatening and uncertain. This cognitive assessment triggers a cascade of physiological reactions that prepare you for fight or flight.
However, if you reframe the situation, viewing it as an opportunity for self-reliance and adventure, your fear may gradually transform into excitement. This shift in cognitive appraisal alters the emotional landscape, empowering you with a sense of control and anticipation.
Cognitive appraisal involves evaluating the situation, identifying its potential impact, and determining its significance for our well-being. This evaluation process is highly subjective and influenced by our beliefs, values, and past experiences.
For example, someone who has faced trauma in the past may be more likely to appraise a harmless situation as dangerous, resulting in an exaggerated emotional response. Conversely, individuals with a positive outlook and strong coping mechanisms may appraise challenging situations as opportunities for growth, leading to more adaptive emotional responses.
In essence, our thoughts act as a filter through which we experience the world. By understanding the role of cognitive appraisal in shaping our emotions, we gain a powerful tool for regulating our emotional responses and fostering greater psychological well-being.
Coping Mechanisms: Mastering the Art of Managing Emotions
As we navigate the labyrinth of life, our emotions ebb and flow, shaping our experiences and testing our resilience. While some emotions provide a momentary rush of joy or a surge of inspiration, others can leave us feeling overwhelmed, depleted, or lost. To thrive in the face of these emotional challenges, we must equip ourselves with effective coping mechanisms.
Understanding Coping Mechanisms
Coping mechanisms are strategies we employ to manage and regulate our emotions. They can be cognitive (involving our thoughts and beliefs), behavioral (involving our actions), or emotional (involving our feelings). The key to successful coping lies in identifying mechanisms that align with our individual needs and situations.
Common Coping Mechanisms
-
Cognitive Coping:
- Problem-Solving: Rationally analyzing the situation and developing solutions.
- Positive Reappraisal: Framing difficult situations in a more optimistic light.
- Seeking Social Support: Confiding in trusted individuals for emotional validation.
-
Behavioral Coping:
- Exercise and Physical Activity: Releasing pent-up energy and reducing stress.
- Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques: Calming the mind and reducing anxiety.
- Distraction: Engaging in activities that take our focus away from negative emotions.
-
Emotional Coping:
- Suppression: Consciously suppressing or avoiding expressing emotions.
- Emotional Expression: Allowing ourselves to freely express our emotions, either verbally or through other outlets.
- Acceptance: Acknowledging and embracing our emotions without judgment.
Effectiveness of Coping Mechanisms
The effectiveness of coping mechanisms varies depending on the individual and the situation. Cognitive coping mechanisms can be helpful for managing stressors that can be logically addressed. Behavioral coping mechanisms can provide immediate relief from unpleasant emotions. Emotional coping mechanisms can help us process and understand our feelings.
Choosing the Right Coping Mechanisms
Choosing the most effective coping mechanisms requires self-awareness and experimentation. By reflecting on our past experiences and identifying what has worked and what hasn’t, we can tailor our coping strategies to our unique needs. It’s important to note that no single coping mechanism is universally effective; the key is to have a repertoire of strategies to draw upon.
Making Coping Mechanisms a Habit
Integrating coping mechanisms into our daily lives is crucial for emotional resilience. By practicing these strategies regularly, even in the absence of immediate emotional distress, we strengthen our ability to cope effectively when challenges arise. It’s like building an emotional toolbox, ensuring we have the necessary tools to navigate the ups and downs of life with greater ease.
Explore Emotional Reactivity and Its Impact on Our Experiences
In the tapestry of human emotions, emotional reactivity emerges as a dominant thread, weaving its influence into the fabric of our experiences. It is an immediate, intense response to internal or external triggers, often characterized by physiological arousal, cognitive distortions, and behavioral impulsivity.
Emotional reactivity can be a protective mechanism, alerting us to potential threats or rewarding positive experiences. However, when it becomes chronic or excessive, it can impair our well-being and hinder our ability to navigate life’s challenges effectively.
Manifestations of Emotional Reactivity
Emotional reactivity can manifest in various ways:
- Cognitive: Distorted thinking, such as catastrophizing or jumping to negative conclusions.
- Physiological: Increased heart rate, sweating, or muscle tension.
- Behavioral: Impulsive actions, such as lashing out or withdrawing socially.
Consequences of Emotional Reactivity
When emotional reactivity is not managed effectively, it can lead to significant consequences:
- Relationship difficulties: It can damage relationships by creating misunderstandings and fostering conflict.
- Physical health problems: Chronic emotional stress can contribute to hypertension, heart disease, and other health issues.
- Mental health concerns: Unchecked emotional reactivity can increase the risk of anxiety, depression, and other mental health disorders.
Managing Emotional Reactivity
Recognizing and managing emotional reactivity is crucial for our well-being. Here are some strategies:
- Identify triggers: Understand what situations or stimuli trigger your emotional reactions.
- Practice self-awareness: Pay attention to your thoughts, feelings, and bodily sensations when you feel emotionally triggered.
- Develop coping mechanisms: Find healthy ways to regulate your emotions, such as deep breathing, meditation, or exercise.
- Seek professional help: If you experience excessive or chronic emotional reactivity, consider seeking therapy from a mental health professional.
Emotional reactivity is an integral part of human experience. By understanding its manifestations, consequences, and strategies for management, we can harness its power for growth and well-being. Remember, the key to emotional health is not the elimination of reactivity but the ability to regulate our responses in a balanced and adaptive manner.
The Hidden Power of Emotional Memory: Shaping Our Past, Present, and Future
Emotions are not merely fleeting sensations; they leave an enduring mark on our psyche, shaping our thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. Emotional memory plays a crucial role in this process, storing and retrieving past emotional experiences to guide our present and future responses.
Imagine a child who experiences a traumatic event. The vivid memories of fear, helplessness, and pain associated with that event become deeply ingrained in their emotional memory. As they grow older, even seemingly innocuous triggers can evoke those intense emotions, causing them to react with anxiety or avoidance. Conversely, positive emotional memories, such as the warmth of a loving embrace, can provide comfort and resilience in challenging times.
Emotional memories are not simply passive repositories of past experiences. They are dynamic and malleable, influenced by our current beliefs, values, and experiences. As we learn and grow, our emotional memories can be modified, allowing us to reinterpret and re-experience past events in a more adaptive way. This process is essential for emotional regulation and healing.
The significance of emotional memory extends beyond its impact on individual experiences. It also plays a role in shaping cultural and societal norms. Collective emotional memories, such as those of historical events or acts of injustice, can influence how people think about themselves, their community, and the world. They can fuel movements for social change or perpetuate cycles of trauma and conflict.
Understanding the power of emotional memory is essential for both personal well-being and social harmony. By acknowledging the influence of past experiences on our present emotions, we gain the ability to manage our emotions more effectively. We can learn from our emotional memories, use them to inform our decisions, and ultimately create a more fulfilling and meaningful life.