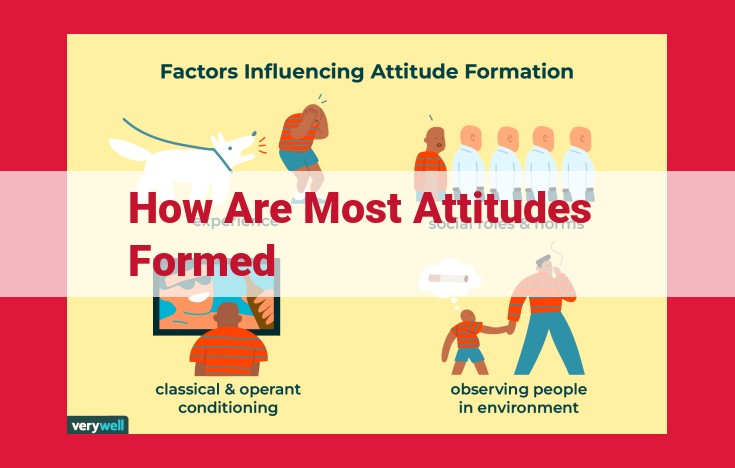
Attitudes, predispositions that color our evaluations of people and objects, are primarily formed through classical conditioning, where paired experiences link certain stimuli with positive or negative responses; through operant conditioning, where behaviors are reinforced or punished, shaping future attitudes; and through modeling, where we learn by observing others’ behaviors and outcomes.
Psychological Factors that Influence Consumer Behavior
- Cognitive Biases: Describe the common cognitive biases that affect consumer decision-making.
- Motivational Factors: Explain the various needs, goals, and desires that drive consumer behavior.
- Emotional Influences: Discuss the role of emotions in influencing consumer choices.
- Self-Perception: Explain how consumers’ self-concept and self-image shape their behavior.
Psychological Factors that Shape Consumer Behavior: A Dive into the Mind of the Consumer
The intricate tapestry of consumer behavior is woven with countless threads, including the psychological forces that drive our decisions. Cognitive biases, for instance, are invisible mental shortcuts that can lead us to make irrational choices. These biases, such as the confirmation bias (tendency to seek information that confirms our beliefs) and the availability heuristic (reliance on easily recalled information), can subtly sway our preferences.
Motivational factors, fueled by our needs, goals, and desires, propel us towards certain products or services. Whether it’s the need for social connection, the pursuit of status, or simply the desire for comfort, our motivations exert a powerful influence on our choices.
Emotions play an equally pivotal role in shaping our consumer behavior. From the joy we feel upon purchasing a coveted item to the anxiety we experience when making a big decision, our emotions are inextricably linked to our shopping experiences. Positive emotions can increase our willingness to spend, while negative emotions can lead us to postpone or abandon purchases.
Finally, our self-perception – our beliefs about who we are and what we value – is a key factor in our consumer behavior. Consumers tend to gravitate towards products and services that align with their self-concept and enhance their self-image. Whether it’s a luxury watch that conveys status or an eco-friendly product that reflects environmental values, our self-perception influences our choices at every turn.
Social Factors Shaping Consumer Behavior
Social factors play a crucial role in molding our consumer habits and influencing our choices. From the moment we’re born, we’re immersed in a social environment that shapes our beliefs, values, and behaviors.
Culture: The Silent Conductor of Consumption
Culture is a powerful force that governs our norms, values, and traditions. It teaches us what’s acceptable and what’s not, what’s desirable and what’s not. These cultural influences deeply impact our consumer behavior. For instance, in cultures that emphasize materialism, people are more likely to spend on luxury goods, while in cultures that value sustainability, consumers prefer eco-friendly products.
Socialization: The Seeds of Consumption
Socialization is the process through which we learn and adopt the behaviors, attitudes, and values of our family, peers, and other social groups. Our primary socialization agents, such as our parents and caregivers, teach us fundamental values and beliefs that shape our early consumer experiences. As we grow older, secondary socialization agents like friends and classmates reinforce and expand our social learning. For example, a child who grows up in a home where healthy eating is emphasized is more likely to adopt healthy eating habits later in life.
Reference Groups: The Power of Belonging
Humans are social beings, and we naturally gravitate towards groups that provide us with a sense of belonging. Reference groups, whether they’re based on age, profession, or lifestyle, have a significant influence on our consumer choices. Aspirational reference groups, for instance, are groups that we aspire to belong to, and their consumption patterns can inspire our own. For example, a young professional might purchase a designer watch to fit in with their colleagues.
Social Media: The Digital Marketplace
In today’s digital age, social media has become an inseparable part of our lives. With billions of users worldwide, these platforms have created a massive marketplace where brands and consumers interact. Social media influencers, with their large and engaged followings, have emerged as powerful opinion leaders, shaping the purchasing decisions of their followers. Moreover, the constant exposure to product recommendations and targeted advertising on social media can subtly influence our consumption patterns.
Environmental Factors Shaping Consumer Behavior
Media Exposure: The Persuasive Power of Advertisements
The world we live in is saturated with countless forms of media, from television commercials to social media ads. These outlets have the power to subtly influence our thoughts, feelings, and ultimately our purchasing decisions. Advertisers meticulously craft their messages to tap into our hopes, dreams, and aspirations, creating a compelling narrative that connects their products with our personal desires. Whether it’s a catchy jingle that gets stuck in our heads or a captivating story that evokes emotions, media exposure exerts a significant impact on our consumer behavior.
Life Experiences: The Past and Present Shaping Our Choices
Our past experiences and current life events also play a crucial role in molding our consumer habits. The memories of positive or negative experiences we’ve had with certain products or brands can shape our perceptions and future choices. For instance, if we’ve had a delightful dining experience at a particular restaurant, we’re more likely to return and recommend it to others. Conversely, if we’ve had a bad experience with a product, we may be hesitant to purchase it again. Life events, such as starting a family or changing careers, can also alter our consumption patterns as our priorities and needs evolve.
Additional Concepts Related to Consumer Behavior
- Attitudes: Describe the nature of attitudes and their impact on consumer behavior.
- Opinion Leaders: Explain the role of opinion leaders in influencing consumer choices.
- Attitude Change: Discuss the factors that can lead to changes in consumer attitudes.
- Persuasion: Describe the strategies used to persuade consumers to change their behavior.
Additional Concepts Shaping Consumer Behavior
Beyond the psychological, social, and environmental factors that influence consumer behavior, several additional concepts play a crucial role in shaping our choices.
Attitudes: The Foundation of Behavior
Attitudes represent our evaluations and feelings towards specific objects, ideas, or behaviors. They are formed through interactions with others, personal experiences, and the media. Our attitudes heavily influence our purchasing decisions, directing us towards products and brands that align with our values and beliefs.
Opinion Leaders: Influencing the Crowd
Opinion leaders are individuals who possess expertise, social status, or popularity and can significantly influence consumer behavior. Their endorsements, reviews, and recommendations can sway the opinions and decisions of others, especially in niche markets or when consumers lack product knowledge.
Attitude Change: Shifting Perspectives & Behaviors
Attitude change refers to the adjustment in our evaluations. This can occur through various factors, such as exposure to new information, persuasive communication, or personal experiences. Marketers and advertisers leverage these factors to change consumer attitudes towards their products or services, ultimately influencing their purchasing decisions.
Persuasion: The Art of Influence
Persuasion involves using specific strategies to change consumer behavior. This can be achieved through emotional appeals, rational arguments, or social proof. Marketers employ various persuasion techniques in advertising campaigns, sales pitches, and online content to convince consumers to purchase their products.
By understanding these additional concepts, businesses can gain valuable insights into the complex factors that drive consumer behavior. This knowledge empowers them to tailor their marketing strategies effectively, influencing consumer attitudes, shaping opinions, and ultimately driving purchasing decisions.